How to Make a Living Testing Strippers
How I Make a Living Testing Strippers
How I Make a Living Testing Strippers
Say what??? Yes, you read right. I make my primary living by testing strippers. I spend 40 hours or more of every week testing strippers, and I enjoy it immensely. Who wouldn't? You may be scratching your head at this point and asking, "How can I make a living doing that?" Well, you can, but the opportunities are limited and you have to be willing to get the training necessary to do the job. It isn't as simple as it sounds.
Perhaps now you are laughing and saying "Is this guy really serious?" Trust me, I'm as serious as a heart attack, but you've jumped to a conclusion which is already most likely incorrect. This is by no means a simple, easy way to make a living. It requires knowledge and commitment.

Copper Dual Damascene Process
What Are Strippers?
What Are Strippers?
Ha, Ha. I know what you are thinking, but you are already way off base. The strippers in this story are what is more commonly referred to as photoresist strippers. To be employed as someone who tests photoresist strippers, you are going to require a minimum of a BS degree in some scientific discipline, ideally, physics. Mine is in biochemistry, but good enough for what I do.
What is Photoresist?
This is a very good question. In the process of building a computer chip (ie integrated circuit), several layers of different materials (sometimes referred to as films) may be stacked on top of each other, but in a computer chip these layers need to be able to communicate with each other. That means that features, such as metal lines, vias, and trenches, must be etched into the surface of various layers. To do that, a mask made of photoresist is applied to the surface of certain layers, and those layers may be sensitive to some specific wavelength of light. The material is then exposed to the wavelength of light to which it is sensitive, and the result is that a pattern is etched into the surface of the material. (This process is called photolithography) But afterward, it is necessary to remove the non-light sensitive mask (ie photoresist). This is done by using a photoresist stripper, but the stripper also must remove the mask without adversely impacting the material on which the mask was applied.
The base layer of a computer chip is ALWAYS silicon. A chip might possibly be several layers thick of alternating metal layers with ILD in between them. ILD otherwise known in "geekese" as inter-layer dielectric, and sometimes there is also a barrier layer inbetween the metal layer and the ILD layer. An inter-layer dielectric is a non-conductive insulating film that separates the metal layers from each other to prevent electrical interference. A barrier layer is a film that prevents electrons from the metal layers from migrating into the dielectric, which is a particular problem with copper. Barrier layers are also usually chemically resistant to a lot of etching materials, so they can be used in places where it is required to etch all of a metal or insulating layer away, but not damage what is underneath.
Even though there is an inter-layer dielectric in between the metal layers, the metal layers still have to be able to communicate with each other, so there may be thousands or millions of tiny holes called "vias" that connect metal layers with each other through the ILD layer, but obviously there has to be some conductive material in those vias, so that the metals can "talk" to each other. Fruequently, those holes might be filled with Tungsten or Titanium plugs.

Before Reading This Article Did You Have Any Idea How a Computer Chip Was Built
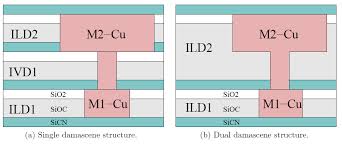
The Copper Damascene Structure
The Copper Damascene Structure
As you can see in the image above, there is a pinkish area between M1-Cu and M2-Cu (Cu is Copper). This area is where the via is, which is plugged with some conductive metal, so the two copper layers can communicate with each other. In the image on the left, you see a layer colled "IVD" which stands for Ion Vapor Deposition. This is a method for depositing a film, rather than the type of film itself, and it could actually be a variety of types of films. Dielectrics films can be of two types. They can be either low-k or high-k. Low-k films are the best insulating films, and have the lowest dielectric constant. You see a film in these images above, called SiO2 which is also known as "thermal oxide," which is a layer that inherently will grow in air on a silicon surface or when the silicon surface is heated. In areas where that layer is not desired, they may be treated with a buffered oxide etchant (a mix of ammonium fluoride and hydrofluoric acid) to remove the SiO2 layer. In other areas it may be desireable to have it there, because it is fairly resistant to many other types of chemicals and it can serve as a protective layer in those cases.

The Stripper Testing Step
The Stripper Testing Step
In order to test a stripper (commercial or developmental), it must meet certain criteria of being able to remove what it is supposed to remove and not damage the ILD or metal layers that may be exposed to it at the same time. The first part of the process is to test to make sure that stripper doesn't damage the metal or the ILD, so we expose those materials to the stripper for some alloted period of time and measure changes in thickness of the material. This is usally done either by measuring changes in resistivity (in the case of metal), or it is done optically (in the case of an ILD). There are several different instrumets manufactured that can do these jobs, but two of the most popular for ILD thickness measurement are the spectroscopic eillipsometer and the NanoMetrics NanoSpec. Of course, there are others too. there also a variety of instrument available that are capable of measuring changes in resistivity (which, BTW is a function of the thickness of the metal).
And that, my friends is how to make a living testing strippers. Just don't forget the part about getting a minimum of a BS degree in a scientific discipline, because most employers in this field will not hire employees without a minimum of a BS degree.
Steps to Becoming a Tester of Strippers
Steps to Becoming a Tester of Strippers
|
|---|
#1. Graduate from High School With a Strong Aptitude for Math and Science Disciplines
|
#2. Graduate from College With a BS in a Science Discipline, Such as Physics, Chemsitry, Biochemistry, or Biology
|
#3. If You Go On To Get a Mater's Degree and/or PhD, You Will Have More Job Opportunities
|
#4. Start Your Job Search. If You Can be Employed Internationally, You Will Have More Job Opportunities.
|
Average Salaries Working in a Semiconductor Laboratry Source: SimplyHired.com
Education Level
| Average Annual Salary
|
|---|---|
BS Degree
| $39,000
|
Master's Degree
| $112,000
|
PhD Degree
| $91,000
|
Why Does a Person With a Master's Degree Earn More Than a PhD?
Why Would a Person With a Master's Degree Earn More Than a PhD in the Semiconductor Industry?
That is a very good question. The answer to that question mostly lies in the fact that the majority of the people in the semiconductor industry who have Master's Degrees are working in the business end, rather than in the laboratory and R&D end of the industry. Those people would be the sales people, accountants, the administrators, and on up to the CEOs of those companies. Personally, my preference is to be working a laboratory, because I don't find number crunching particularly interesting, but many people do, and that is fine. You have to make your own decisions what you are best fitted for. If you attain a BS degree and get a job within the semiconductor industry, many companies will pay all or part of continuing education as long as you maintain the grade standards they have set to receive tution reimbursement. Most companies won't pay your tuition upfront, but even part-time students are still eligible for student loans, which are still at relatively low interest rates compared with other types of loans.
If this type of work looks like you might find it interesting, I would say to you "Go for it." It's never too late to learn new things. I did not start college until I was 40 years old, and I went part-time for 10 years in order get my degree finally at 50 years old. If had to do it over again, I would have gone back to school much earlier, but family has to always be the first priority.






